设备网格入门¶
Created On: Jan 24, 2024 | Last Updated: Feb 24, 2025 | Last Verified: Nov 05, 2024
作者: Iris Zhang, Wanchao Liang
先决条件:
Python 3.8 - 3.11
PyTorch 2.2
为分布式训练设置分布式通信器,即 NVIDIA 集体通信库 (NCCL) 通信器,可能会带来显著的挑战。对于需要组合不同并行解决方案的工作负载,用户需要为每个并行解决方案手动设置和管理 NCCL 通信器(例如 ProcessGroup)。这个过程可能会很复杂并且容易出错。DeviceMesh 可以简化这个过程,使其更加易于管理且不易出错。
什么是 DeviceMesh¶
DeviceMesh 是一个管理 ProcessGroup 的高级抽象。它允许用户从容创建节点间和节点内的进程组,而无需担心如何为不同的子进程组正确设置排名。用户还可以通过 DeviceMesh 轻松管理用于多维并行的底层进程组/设备。
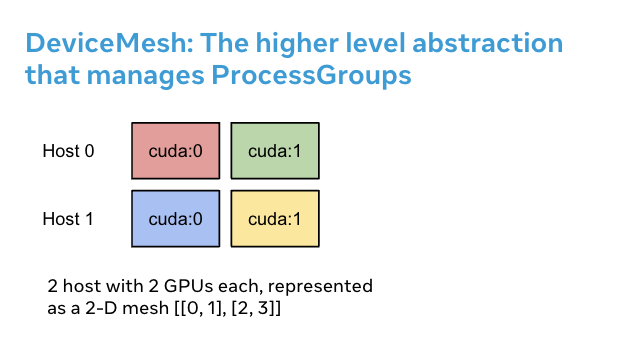
DeviceMesh 的作用¶
在工作中需要多维并行(即 3D 并行),并且要求并行组合时,DeviceMesh 非常有用。例如,当你的并行解决方案需要既跨主机通信又在每个主机内通信时。上图显示我们可以创建一个 2D 网格连接每个主机内的设备,并在同一设置下连接其他主机设备的对应部分。
没有 DeviceMesh,用户需要手动设置 NCCL 通信器、每个进程上的 CUDA 设备,然后才能应用任何并行解决方案,这可能非常复杂。以下代码片段展示了没有使用 DeviceMesh 的混合分片 2D 并行模式设置。首先,我们需要手动计算分片组和复制组。然后,我们需要将正确的分片组和复制组分配给每个排名。
import os
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
# Understand world topology
rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
print(f"Running example on {rank=} in a world with {world_size=}")
# Create process groups to manage 2-D like parallel pattern
dist.init_process_group("nccl")
torch.cuda.set_device(rank)
# Create shard groups (e.g. (0, 1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6, 7))
# and assign the correct shard group to each rank
num_node_devices = torch.cuda.device_count()
shard_rank_lists = list(range(0, num_node_devices // 2)), list(range(num_node_devices // 2, num_node_devices))
shard_groups = (
dist.new_group(shard_rank_lists[0]),
dist.new_group(shard_rank_lists[1]),
)
current_shard_group = (
shard_groups[0] if rank in shard_rank_lists[0] else shard_groups[1]
)
# Create replicate groups (for example, (0, 4), (1, 5), (2, 6), (3, 7))
# and assign the correct replicate group to each rank
current_replicate_group = None
shard_factor = len(shard_rank_lists[0])
for i in range(num_node_devices // 2):
replicate_group_ranks = list(range(i, num_node_devices, shard_factor))
replicate_group = dist.new_group(replicate_group_ranks)
if rank in replicate_group_ranks:
current_replicate_group = replicate_group
为了运行上述代码片段,我们可以利用 PyTorch Elastic。创建一个名为 2d_setup.py 的文件。然后运行以下 torch elastic/torchrun 命令。
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --rdzv_id=100 --rdzv_endpoint=localhost:29400 2d_setup.py
备注
为了简化演示,我们仅使用一个节点模拟 2D 并行。请注意,此代码片段也适用于运行在多主机设置。
借助 init_device_mesh(),我们可以仅用两行完成上述的 2D 设置,并且如果需要,我们仍可以访问底层的 ProcessGroup。
from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
mesh_2d = init_device_mesh("cuda", (2, 4), mesh_dim_names=("replicate", "shard"))
# Users can access the underlying process group thru `get_group` API.
replicate_group = mesh_2d.get_group(mesh_dim="replicate")
shard_group = mesh_2d.get_group(mesh_dim="shard")
创建一个名为 2d_setup_with_device_mesh.py 的文件。然后运行以下 torch elastic/torchrun 命令。
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 2d_setup_with_device_mesh.py
如何将 DeviceMesh 与 HSDP 一起使用¶
混合分片数据并行 (HSDP) 是一种在主机内执行 FSDP 并在主机间执行 DDP 的 2D 策略。
让我们看一个示例,了解 DeviceMesh 如何帮助应用 HSDP 到你的模型上的简单设置。有了 DeviceMesh,用户无需手动创建和管理分片组和复制组。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
from torch.distributed.fsdp import FullyShardedDataParallel as FSDP, ShardingStrategy
class ToyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ToyModel, self).__init__()
self.net1 = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.net2 = nn.Linear(10, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net2(self.relu(self.net1(x)))
# HSDP: MeshShape(2, 4)
mesh_2d = init_device_mesh("cuda", (2, 4))
model = FSDP(
ToyModel(), device_mesh=mesh_2d, sharding_strategy=ShardingStrategy.HYBRID_SHARD
)
创建一个名为 hsdp.py 的文件。然后运行以下 torch elastic/torchrun 命令。
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 hsdp.py
如何将 DeviceMesh 应用于自定义并行解决方案¶
在处理大规模训练时,你可能有更复杂的自定义并行训练组合。例如,你可能需要为不同的并行解决方案切片子网格。DeviceMesh 允许用户从父网格中切出子网格并重用在初始化父网格时已经创建的 NCCL 通信器。
from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
mesh_3d = init_device_mesh("cuda", (2, 2, 2), mesh_dim_names=("replicate", "shard", "tp"))
# Users can slice child meshes from the parent mesh.
hsdp_mesh = mesh_3d["replicate", "shard"]
tp_mesh = mesh_3d["tp"]
# Users can access the underlying process group thru `get_group` API.
replicate_group = hsdp_mesh["replicate"].get_group()
shard_group = hsdp_mesh["shard"].get_group()
tp_group = tp_mesh.get_group()